Cardiovascular Imaging
Diagnostic RadiologyWithin our Cardiothoracic Imaging Division, we provide the full spectrum of imaging procedures of the cardiovascular and thoracic system, including the latest CT and MRI technology, providing the highest resolution with the lowest side effects. Our services are provided both at the Campus in Freiburg as well as at the University-Heart-Center in Bad Krozingen.

Cardiac Computed Tomography (Cardiac CT): Latest CT-Technology provides non-invasive visualization of the coronary arteries as well as the detection of coronary stenosis and plaque. As such, cardiac CT can be performed with high value to rule out the presence of coronary artery disease according to current guidelines. The examination is painless and can be carried out on an outpatient basis. The patient lies on the examination table and is connected to an electrocardiograph and an intravenous line. The scan takes only a few seconds. If necessary, a drug reducing the heart rate will be administered. The entire imaging including all preparations will take about 10 minutes.
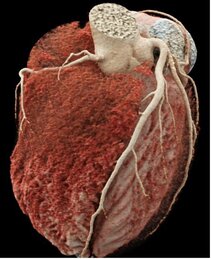
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CMRI): CMRI is particularly valuable in assessing the heart muscle with respect to global and regional contraction, function, perfusion, and characterization of the tissue with respect to i.e. ischemia / heart attack, inflammation, or functional impairment. As such, MRI is critical in diagnosing a large number of diseases affecting the heart and determining subsequent treatment options.