Imaging
Modern high-resolution visualization diagnostics plays a key role in determining the brain area where the epileptic seizures originate and in defining the etiologies of seizures in case of focal epilepsy. In addition, there are more and more opportunities for brain function mapping by means of functional neuroimaging.
Over the recent years the structural and functional visualization diagnostics has acquired the substantial significance in diagnostics, especially in case of focal epilepsy. In an increasing number of cases by means of the enhanced magnetic resonance imaging scanners it has become possible to detect the potential reason of the focal epilepsy which is mapped as an affected area during the MRI procedure. Computer-based post-processing methods can increase the sensitivity to detect subtle abnormalities of the cerebral cortex.
Functional visualization methods which register the metabolic activity or the brain blood circulation between or during the epileptic seizures help to elicit even more essential features of epileptic focus localization. The functional magnetic resonance imaging gives additional important information about the functionally significant brain areas and their connectivity.
In Freiburg in the Department of Neuroradiology as well as in the Department of Medical Physics there are latest generation 3T-MRI scanners for the structural and functional high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. The research of brain functions among the patients with epilepsy is performed in cooperation with the Department of Nuclear Medicine.
High-resolution 3T MRI (Simens Prisma) in the Department of Neuroradiology with epilepsy-specific sequences

SPECT-camera (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) for the measurement of functional parameters between and during the epileptic seizures in the Department of Stereotactic Neurological Surgery
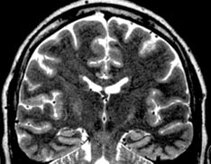
Sensitive detection of the mild hippocampal alterations (Department of Medical Physics)
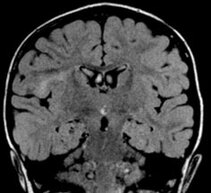
Detection of neuronal migration abnormality (cortical dysplasia)
Department of Neuroradiology

MR-postprocessing: Voxel-based morphometriy to detect subtle brain abnormalities
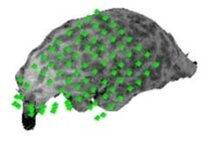
The image of electrode grid position made by means of curvilinear reformatting
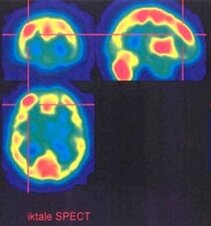
Ictal hyperperfusion in SPECT in case of cryptogenic frontal focal-cortical dysplasia (Department of Nuclear Medicine)
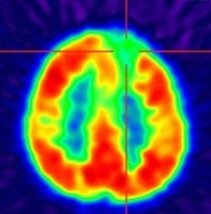
FDG-PET for hypometabolic area detection (here: focal-cortical dysplasia in the frontal part on the left side) (Department of Nuclear Medicine)
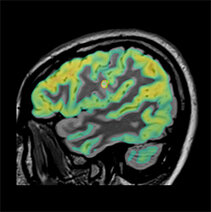
Multimodal image fusion
Fusion of structural and functional imaging improve the sensitivity of detections of subtle epileptogenic areas.