Surgical Treatment
Epilepsy surgery is undertaken at the Department of General Neurosurgery of the Neurocentre. Considerable experience with the complete range of surgical forms of intervention has been collected. In the following, the surgical procedures are considered individually.
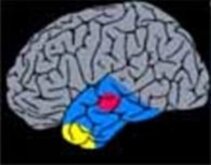
1. Temporal Lobectomy/Topectomy
Removal of the temporal lobe or of specific areas by a lateral site of entry. This can be carried out in conjunction with a Amygdalohippocampectomy
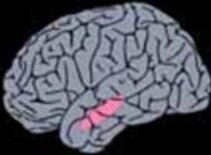
2. Selective Amygdalohippocampectomy
Exclusive removal of epileptogenic temporomesial areas by a transsylvian site of entry

3. Laser interstitial thermotherapy (LITT)
Laser-based interstitial thermotherapy is a minimal invasive procedure replacing open neurosurgery in selected cases (e.g. hippocamapal sclerosis or heterotopias). The epileptogenic lesion is inactivated under MR imaging control via a stereotactically guided lased probe. This particularly mild procedure allows to shorten the duration of in-patient stay.
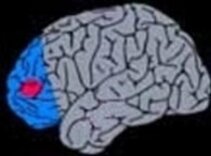
4. Extratemporal Lobectomy/Topectomy
Removal of a lobe on the brain or a specific resection of the epileptogenic zone within the lobe
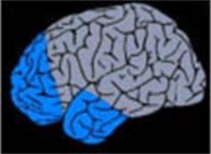
5. Multilobectomy
Resection of specific alterations in several brain lobes
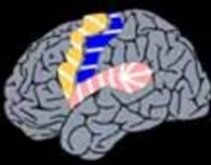
6. Multiple subpiale Transsections
Transection of horizontal nerve fibre connections (needed to spread seizure) while maintaining the vertical connections (responsible for the function)
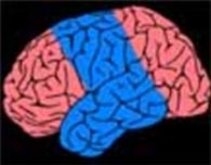
7. Hemispherectomy/ Hemispherotomy
Disconnection of the diseased (epileptogenic) hemisphere
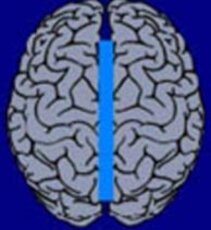
8. Callostomy
Palliative procedure that hinders the spread of the epileptic event from the one to the other hemisphere by transection of the corpus callosum

9. Stereotactic Thermocoagulation
Stereotactic thermocoagulation is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to disconnect epileptogenic lesions. Freiburg is one of the world largest centers applying this method to treat epilepsies arising from Hypothalamic Hamartomas

10. Implantation of a vagus nerve stimulator
Neurostimulatory treatment to avoid spread of epileptic activity across the brain. Modern devices allow for a stepped and individualized programming of neurostimulation pulses.

11. Implantation of a Focal Cortex Stimulator (EASEE-System)
Epicranial stimluation of the epileptic focus is a new neurostimulation method which has become CE-certified in 2022 and was developed in Heidelberg and Freiburg. The electrode is implanted below the skin of the head over the epileptic focus, and stimulation is not perceived by the patient.