Epilepsy Surgery
NeurosurgeryThe Epilepsy Center offers a comprehensive program for the diagnosis and treatment of severe forms of epilepsy. Of special importance is the pre-surgical diagnosis of epilepsy using differentiated anatomical and functional imaging methods, as well as electrophysiological techniques of long-term video-EEG monitoring with non-invasive and invasive recordings. Apart from the classical resective procedures, the surgical program for epilepsy includes selective operation methods, as well as the techniques of stimulation. The conservative and surgical treatment of complex children epilepsies including hemispherotomy is currently a special field of activity.
The following surgical procedures are available:
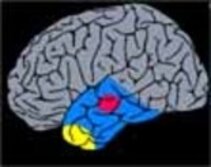
1. Temporal Lobectomy/Topectomy
Removal of the temporal lobe or of specific areas by a lateral site of entry. This can be carried out in conjunction with a Amygdalohippocampectomy
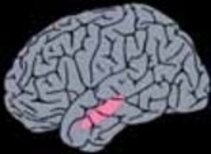
2. Selective Amygdalohippocampectomy
Exclusive removal of epileptogenic temporomesial areas by a transsylvian site of entry
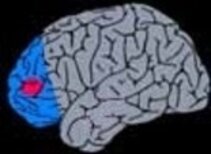
3. Extratemporal Lobectomy/Topectomy
Removal of a lobe on the brain or a specific resection of the epileptogenic zone within the lobe
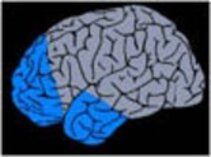
4. Multilobectomy
Resection of specific alterations in several brain lobes
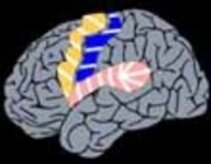
5. Multiple subpiale Transsections
Transection of horizontal nerve fibre connections (needed to spread seizure) while maintaining the vertical connections (responsible for the function)
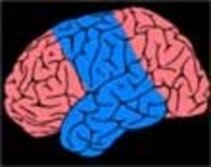
6. Hemispherectomy/ Hemispherotomy
Disconnection of the diseased (epileptogenic) hemisphere
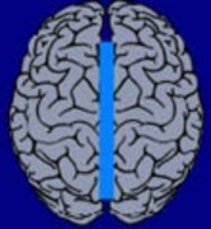
7. Callostomy
Palliative procedure that hinders the spread of the epileptic event from the one to the other hemisphere by transection of the corpus callosum

8. Implantation of a vagus stimulator
Procedure that should hinder the formation of this seizure by inducing desynchronisation of electric activity in the brain