What are CT/ MRI/ Angiography?
What is Computed tomography (CT Imaging)
X-ray computed tomography (CT Scan)
is a very fast examination method allowing quick and reliable examination of all body parts, including whole-body imaging within less than 5 minutes – at sub-millimeter resolution.
Dual Source - CT Imaging
Recently, a method has been developed which allows to identify different types of tissue on CT scans with the help of “Dual Energy” (DE) computed tomography. The computer tomograph has two X-ray tubes capable of producing two different radiation energies. With this method, tissue and fluids can be visualized, while at the same time vessels, bones and soft tissue are better differentiated.
The Dual Energy method makes multiple examinations unnecessary and also opens up new fields of clinical application for computed tomography. In cardiological examinations, parts of the myocardium cut off from blood supply can be marked in different colours. Thus the blood supply of the heart after an infarction can be evaluated in order to find out which areas of the organ have been damaged.
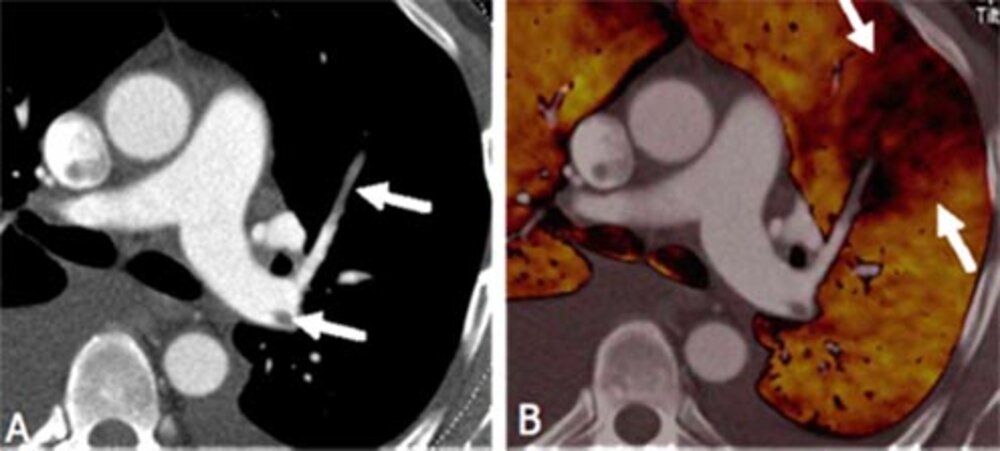
Blood clots in central pulmonary circulation (A). In contrast to the conventional method, Dual Energy CT can also visualize the pulmonary blood flow. In (B) a wedge-shaped blood-flow deficit is discernible behind the blood clot.
If pulmonary embolism – sudden occlusion of blood vessels in the lung - is suspected, pulmonary vessels not supplied with blood can be identified with colour markings. This examination technique allows to detect even initially asymptomatic occlusions of small pulmonary vessels and to treat them before potential complications develop. With Dual Energy CT it is also possible to analyze the biochemical composition of kidney stones from uric acid or, e.g., calcium oxalate.
What is MRI Imaging?
An MRI Scan is a detailed examination of affected organs. Via a magnetic field, it allows for the precise evaluation of most medical conditions without x-ray exposure.
What is angiography?
Angiography is an examination of the vessels using X-Ray imaging, an injection of contrast agents and a catheter. It is especially necessary to detect vessel narrowing or other abnormalities.
The advantage of angiography is that it combines diagnosis and treatment in one procedure. During an angiography, we can treat the vessel (stents) and perform minimal invasive tumor treatments.